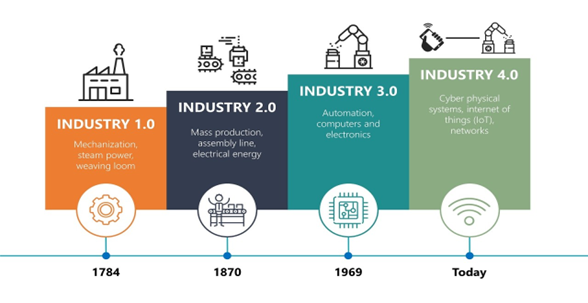
Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, is the ongoing transformation of traditional industries through the use of smart technology. It involves integrating digital technologies like automation, robotics, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) into manufacturing processes to make them more efficient, connected, and adaptable. It’s like making factories and industries smarter and more capable of handling complex tasks with less human intervention.
Advanced CNC
Advanced CNC/VMC refers to advanced Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology applied specifically to Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs). VMCs are a type of machine tool used for various manufacturing processes, such as milling, drilling, and cutting, where the cutting tool moves vertically against the workpiece. Advanced CNC/VMC systems utilize sophisticated computer controls to precisely program and automate these machining operations, allowing for high levels of precision, efficiency, and flexibility in production. In essence, it’s using advanced computer technology to control and optimize the performance of vertical machining centers for manufacturing tasks.
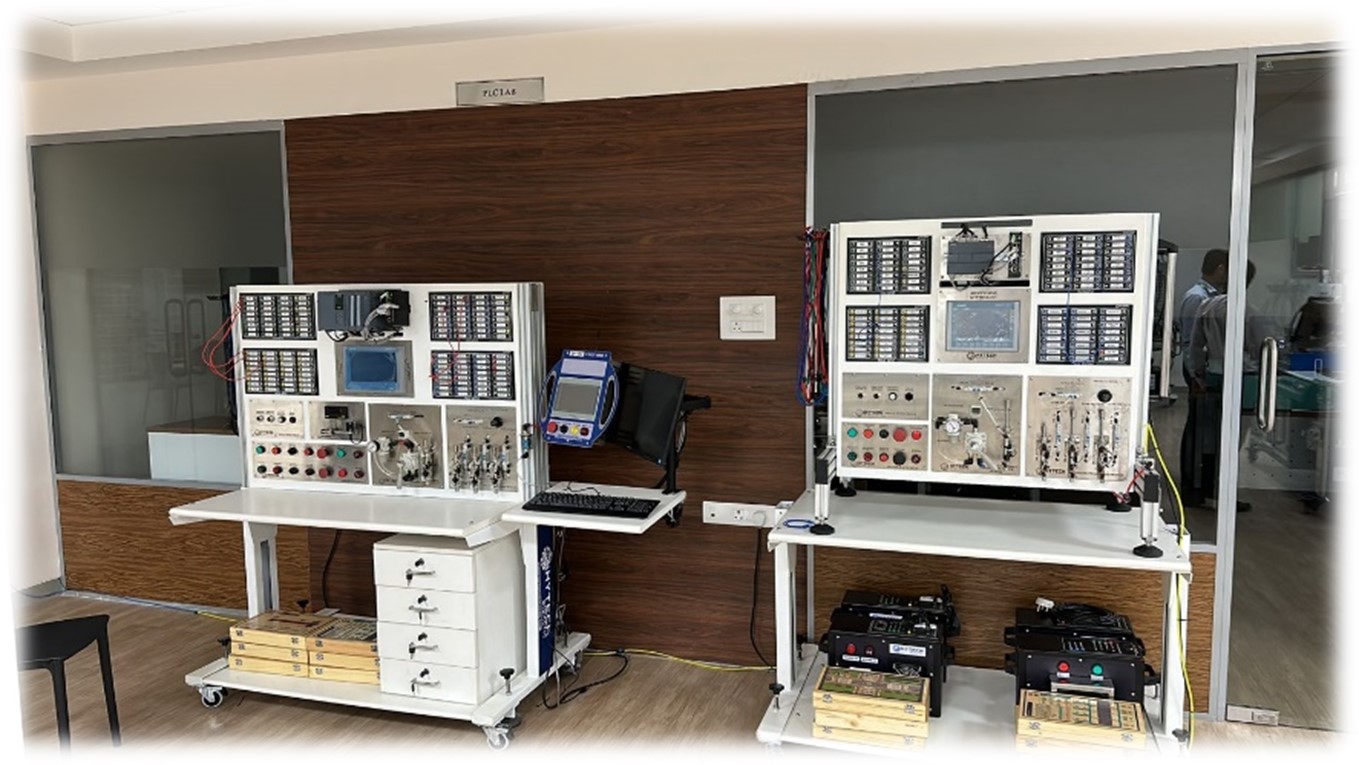


PLC & Automation
The technology or process of controlling and operating machinery or processes without human intervention. It involves using various technologies such as PLCs, sensors, robotics, and computer systems to perform tasks traditionally done by humans. The goal of automation is to improve efficiency, accuracy, and safety while reducing human labor and error. PLCs play a central role in automation by providing the logic and control necessary to coordinate and execute automated processes. PLCs are programmed to control and automate electromechanical processes such as assembly lines, robotic devices, or any machinery requiring precise control. They receive inputs from sensors or switches, process the information according to a programmed logic, and then produce outputs to control actuators or other devices.
Smart Factory
A Smart Factory is a manufacturing facility where machinery and equipment are interconnected through the Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced automation technologies. These technologies enable real-time data exchange, analysis, and decision-making, leading to highly efficient and flexible production processes. In simpler terms, a Smart Factory is like a super-smart version of a traditional factory, where machines, robots, and systems communicate with each other to optimize operations, minimize downtime, and adapt quickly to changes in production requirements.

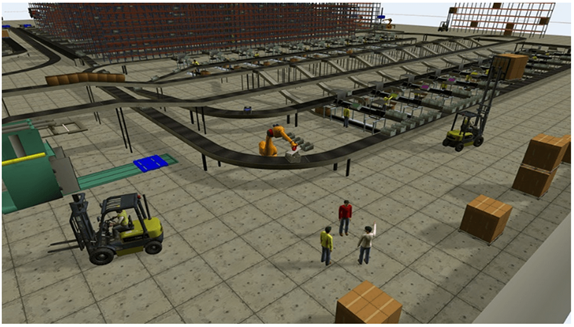
Digital Twin
A virtual representation or model of a physical manufacturing facility. It incorporates real-time data from various sources within the factory, such as sensors, machines, and processes, to create a digital replica of the physical environment. This digital twin allows manufacturers to simulate and analyze different scenarios, optimize processes, and predict outcomes without impacting the actual production line. Essentially, it’s like having a digital counterpart of the factory that can be used for testing, monitoring, and improving operations, leading to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and better decision-making.
Al Robotics
Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies into robotics systems. AI enables robots to perceive, learn, adapt, and make decisions autonomously, allowing them to perform tasks more efficiently and effectively. These AI-powered robots can be used in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, and logistics, to automate processes, enhance productivity, and improve outcomes. Examples of AI robotics applications include autonomous vehicles, robotic surgery, warehouse automation, and intelligent manufacturing systems.


3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital model or design. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods that involve cutting away material from a solid block, 3D printing adds material layer by layer until the final object is formed.Top of Form
3D printing has revolutionized manufacturing by enabling rapid prototyping, customization, and on-demand production of complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. It is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, architecture, and consumer goods, for applications such as prototyping, tooling, production parts, medical implants, and architectural models.
Internet of Things
IoT is an ecosystem of devices, sensors, applications, and associated networking equipment that work together to collect, monitor, and analyze data from industrial operations. Analysis of such data helps increase visibility and enhances troubleshooting and maintenance capabilities. It can also increase efficiencies, reduce costs, and improve safety and security. IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) connects machines and devices in industries such as manufacturing, transportation, oil and gas, power generation and transmission, mines, and ports.

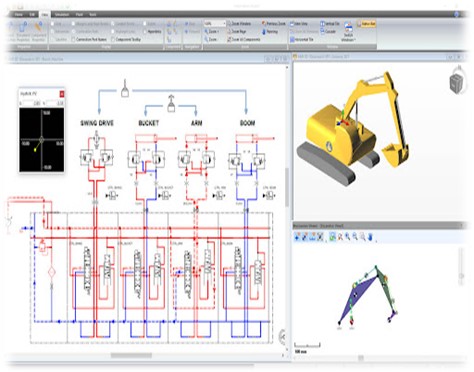
Simulation
Simulation is the process of creating a virtual representation or model of a real-world system, process, or phenomenon. It involves using software or mathematical models to imitate the behavior of the actual system under different conditions or scenarios.
In simulation, various parameters and variables can be adjusted and manipulated to observe their effects on the system’s performance or outcomes. This allows engineers, scientists, designers, and decision-makers to analyze, test, and optimize systems in a controlled and cost-effective environment before implementing changes in the real world.
Integration
Industry 4.0 integration involves merging advanced technologies like Big Data, IoT, AI, and automation into manufacturing processes. Smart factories utilize connected sensors to gather data on equipment performance and production metrics. This data is analyzed in real-time using Big Data analytics and AI algorithms to optimize operations, predict maintenance needs, and improve efficiency. IoT devices enable seamless communication between machines and systems, facilitating better decision-making and enabling agile production processes. Overall, Industry 4.0 integration aims to create intelligent, interconnected systems that drive productivity, reduce costs, and enable innovative manufacturing approaches.
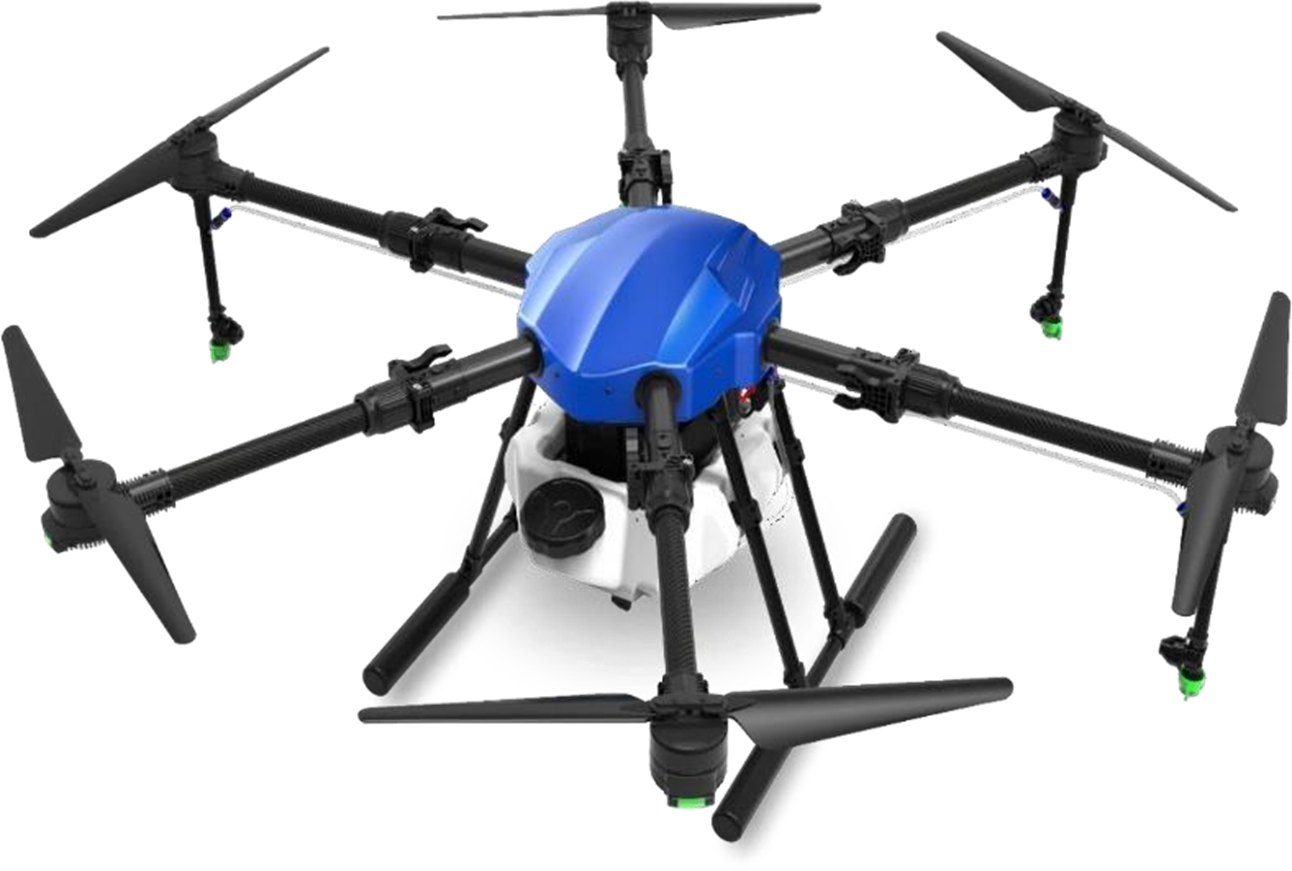


Drone
Drone technology, also known as unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technology, has seen significant advancements in recent years across various fields, including military, commercial, recreational, and humanitarian sectors. In the future, drone technology will advance significantly, offering increased autonomy, swarm intelligence, and applications in urban air mobility, delivery services, environmental monitoring, space exploration, and security.